In a report from AT&T, 80% of businesses acknowledged they experienced some sort of a cyber attack. For today’s companies, falling victim to one of these attacks is no longer a question of “if” but “when.” Today’s employees are connected to the Internet all day every day, communicating with colleagues and stakeholders, sharing critical information and jumping from site to site. With hackings, data breaches and ransomware attacks on the rise, it is essential for all companies to plan for the worst, with mandatory cybersecurity trainings for all employees and with the recommended solutions for mitigating the risks.
Read about Cybersecurity for small to medium businesses.
Cybersecurity Training for Employees
According to over 1,700 IT service providers, the lack of cybersecurity awareness amongst employees is a leading cause of a successful ransomware attack against an SMB. That being said, employee training is a top component of a successful cybersecurity protection program and most likely the only way to ensure all staff understand the cyber threats they face and, most importantly, what they should look for in order to avoid falling victim to them
Cyber Scams 101
At the root of the majority of ransomware attacks is the tactic of social engineering,
leveraged by hackers, which involves manipulating a person or persons in order to
access corporate systems and private information. Social engineering plays into human nature’s inclination to trust. For cyber criminals, it is the easiest method for obtaining access to a private corporate system. After all, why would they spend the time trying to guess someone’s password when they can simply ask for it themselves?
Let’s help employees help themselves. Below is a quick and dirty overview of today’s
most common and effective social engineering scams. This is the list to hand
employees on their very first day. Why not include it in their “Welcome” packet? If they
don’t know these leading hacker tactics, they WILL fall for them.
Click here to read about top data breaches and Cybersecurity attacks in 2021.
3 types of Social Engineering Scams to Know
Employee awareness of social engineering is essential for ensuring corporate cybersecurity. If end users know the main characteristics of these attacks it is much more likely they can avoid falling for them. As many of use are visual learners, make sure to provide them with actual examples of these scams.
Phishing: The leading tactic leveraged by todays ransomware hackers, typically delivered in the form of an email, chat, web ad or website designed to impersonate a real system and organization.
Baiting: Similar to phishing, baiting involves offering something enticing to an end user in exchange for private data. The “bait” comes in many forms, both digital, such as a music or movie download, and physical, such as a branded flash drive labeled “Executive Salary Summary Q3 2016” that is left out on a desk for an end user to find. Once the bait is taken, malicious software is delivered directly into the victim’s computer.
Tailgating: is when an unauthorized person physically follows an employee into a restricted corporate area or system. The most common example of this is when a hacker calls out to an employee to hold a door open for them as they’ve forgotten their RFID card
How to Spot a Cyber Scam
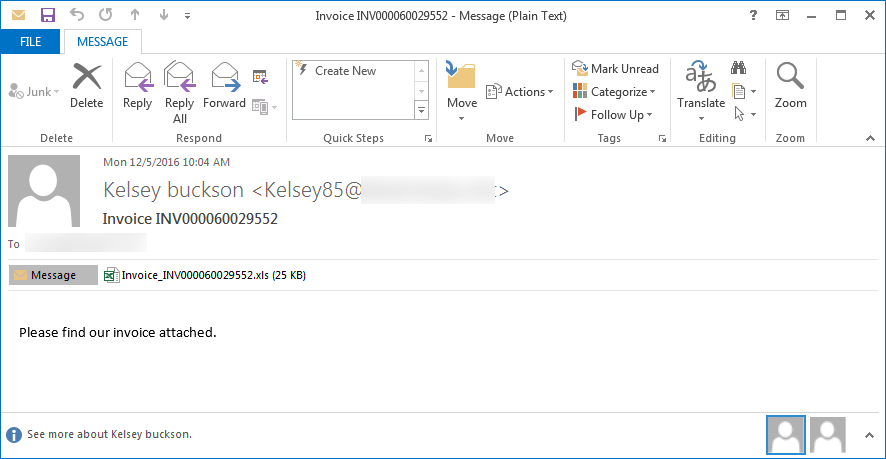 Inbox Scams
Inbox Scams
The image above is a prime example of a phishing email used to spread Locky, a common strain of ransomware. To the recipient, the email appears to come from a business partner asking the reader to “see the attached invoice” by clicking on the attached Word doc. Note how harmless this email appears and how easy it would be for a user to absentmindedly open and click, an action that would result in an
instant ransomware infection. It happens every single day
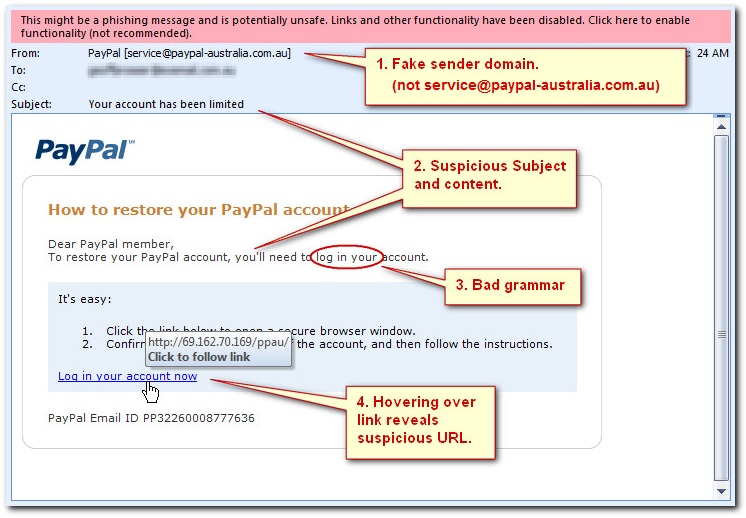 Red Flags
Red Flags
Missing sender or recipient information, generic greetings, misspelled
email addresses (i.e., billing@amzaon.com), and email addresses that don’t match the company name. Any emails that ask the recipient to download a form or macro in order to complete a task are highly suspicious and an employee should NOT click on anything. Instead, report the email to IT immediately.
Learn more about information security- Cyber Security 101 guide.
Essential Cybersecurity Solutions
Here’s one thing the cybersecurity world can agree on: there is no single product available today that will solve all of your cybersecurity problems. In today’s world, it takes many technologies and processes to provide comprehensive risk and security management. Instead, organizations should continually be checking their systems for vulnerabilities, learning about new threats, thinking like attackers and adjusting their defenses as needed.
Must-Have Solutions for Cyber Protection: Layered Security
Antivirus Software
Cybersecurity technology starts with antivirus software. Antivirus, as its name implies, is designed to detect, block, and remove viruses and malware. Modern antivirus software can protect against ransomware, keyloggers, backdoors, rootkits, trojan horses, worms, adware, and spyware. Some products are designed to detect other threats, such as malicious URLs, phishing attacks, social engineering techniques, identity theft, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Firewalls
A network firewall is also essential. Firewalls are designed to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of configurable rules—separating your secure internal network from the Internet, which is not considered secure. Firewalls are typically deployed as an appliance on your network and in many cases offer additional functionality, such as virtual private network (VPN) for remote workers.
Password Management
Recent studies have reported that weak passwords are at the heart of the rise in cyber theft, causing 76% of data breaches. To mitigate this risk, businesses should adopt password management solutions for all employees. Many people have a document that contains all of their password information in one easily accessible file—this is unsafe and unnecessary. There are many password management apps
available today. These tools allow users keep track of all your passwords, and if any of your accounts are compromised you can change all of your passwords quickly. Encryption is also an important consideration. Encrypting hard drives ensures that
data will be completely inaccessible, for example if a laptop is stolen.
Backup and Recovery
Taking frequent backups of all data considered critical to your business is critical.
The exact frequency of backups will vary based on your business’ specific needs.
Traditionally, most businesses took a daily backup, and for some businesses this
may still be suitable. However, today’s backup products are designed to make
incremental copies of data throughout the day to minimize data loss. When it
comes to protecting against cyber attacks, solutions that back up regularly allow
you to restore data to a point in time before the breach occurred without losing all
of the data created since the previous night’s backup.
Click here to find the top ten questions to ask to your Cyber-security vendor.
Conclusion
Today’s data threats don’t discriminate; businesses of all sizes are susceptible to attacks. However, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) are often less prepared to deal with security threats than their larger counterparts. The reasons for this vary from business to business, but ultimately it comes down to the fact that SMBs often have less resources to devote to cybersecurity efforts.
Organizations must be certain that employees understand the risk and embrace safe
browsing habits, making sure they are accessing sites using the HTTPS secure communication protocol and being wary of any site asking for private information. Additionally the organization itself must implement essential cybersecurity solutions to protect confidential data and prevent cybersecurity attacks.
For help planning and implementing your organization's cybersecurity plan, contact a representative today.



