With consumers increasingly relying on web applications to purchase items, check email, pay rent, and more, the risk of a sensitive data breach has never been higher. It is crucial for organizations to ensure that their website is fully protected to increase productivity and protect themselves and their customers against emerging security threats. If your website collects any customer data, it's up to you to protect them from cybercriminals.
What is a Web Application Firewall?
-png.png) Web Application Firewalls, or WAF, block an ever-expanding list of sophisticated web-based intrusions and attacks that target the applications hosted on web servers and the sensitive or confidential data to which they have access.
Web Application Firewalls, or WAF, block an ever-expanding list of sophisticated web-based intrusions and attacks that target the applications hosted on web servers and the sensitive or confidential data to which they have access.
How does a Web Application Firewall Work?
Just as your organization's firewall stand as a shield around your IT infrastructure to filter traffic and protect against cybercriminals, your WAF is a firewall that shields your web applications from the same kind of malicious activity. A WAF protects by monitoring the HTTP traffic and filtering out malicious activity to prevent it from reaching the server. WAFs run off a set of policies to help determine what traffic is malicious by indicating what vulnerabilities and traffic behavior to identify.
WAFs can be configured into three general models: Whitelisting, Blacklisting, and Hybrid. Whitelisting tells the WAF to only allow in traffic that has been pre-approved and meets specified criteria. Blacklisting is configured to block known vulnerabilities and malicious signatures but allow all other traffic. Hybrid is configured to incorporate both whitelisting and blacklisting methods for the specific need of the web application. Each of these configurations has pros and cons depending on what your web application is used for. Your internal IT Team or IT partner can set up a configuration that will work best for your specific web applications. Chat with us today to see if a WAF is right for you organization.
Click here and see why multi-layered security is your best defense against Ransomware.
Types of Web Application Firewalls
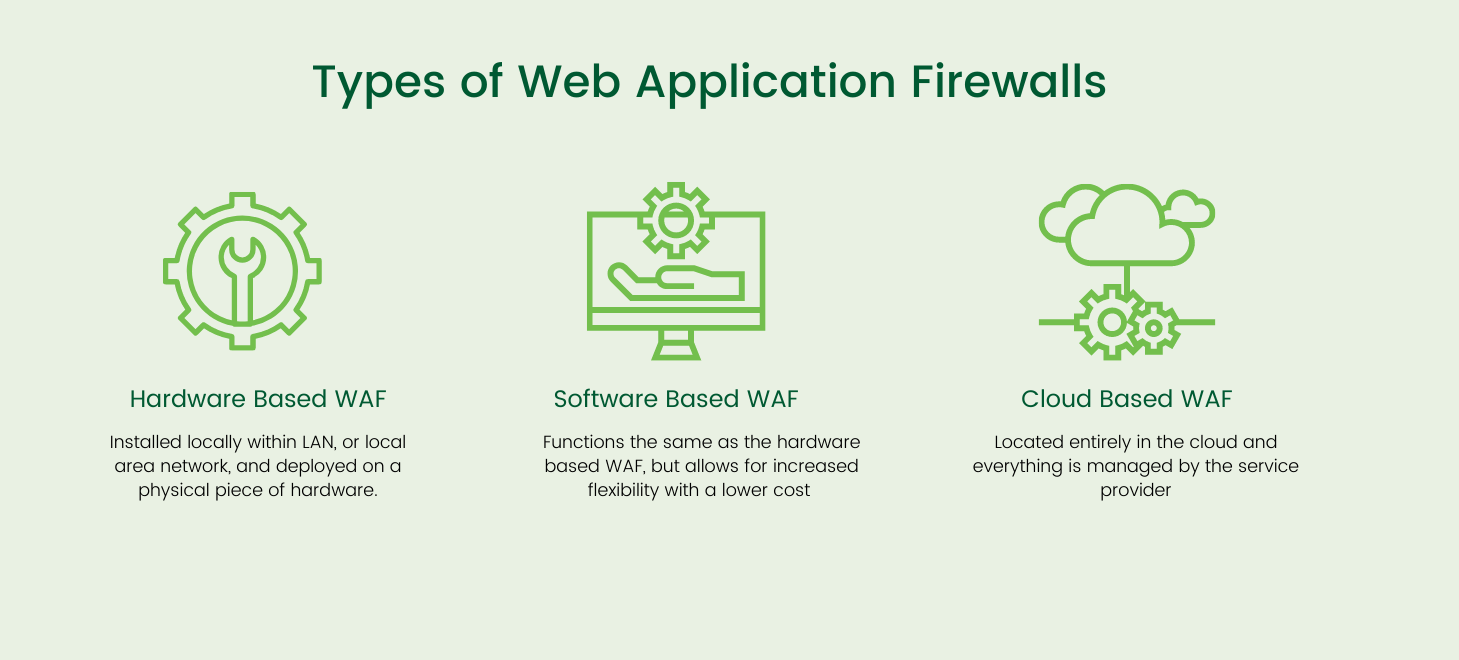 There are three types of WAFs available on the market. They all accomplish the same goal but are installed and deployed in different locations. Because of this, the three types differ in cost, maintenance required, and speed. One is not inherently better than another, so it is up to your IT team or managed service provider to determine which option will be best for your organization's needs.
There are three types of WAFs available on the market. They all accomplish the same goal but are installed and deployed in different locations. Because of this, the three types differ in cost, maintenance required, and speed. One is not inherently better than another, so it is up to your IT team or managed service provider to determine which option will be best for your organization's needs.
Hardware-based WAF
A hardware based WAF is one that is installed locally within LAN, or local area network, and deployed on a physical piece of hardware. The operating system runs within the appliance and supports any updates for the WAF. Because this option runs on a piece of hardware, there are automatically pros and cons that go along with it. Owning and maintaining physical equipment is expensive, making it a higher cost than other WAF types, but because of its close proximity to the server this option has high performance and speed. This option may be best for organizations who have a large number of clients and high daily web traffic.
Software-based WAF
A software based WAF is installed in a Virtual Machine, or VM, rather than hardware. This option functions the same as the hardware based WAF, but allows for increased flexibility as it can be used on-prem or in the cloud and has a decreased cost because there is no hardware required. The software based WAF, however, does increase time to monitor and filter traffic which slows the web application. This option may be best for small to mid-size organizations that need to protect themselves while keeping costs down.
Cloud based WAF
A cloud based WAF is offered as a SaaS, or software as a service, structure. With this option, the WAF is located entirely in the cloud and everything is managed by the service provider. This creates the most simple way for organization's to deploy and maintain a WAF as the service provider will optimize and update as needed. This option may be best for organizations that have limited IT resources to maintain and manage their WAF.
Who needs a Web Application Firewall?
Does your organization have a website or other web applications? If you answered yes, then you should consider using a WAF. Even small websites are a target for cybercriminals, especially since this type of security is often neglected in small organizations, putting you at risk regardless of how unlikely you perceive it to be.
Nearly 70% of all websites use HTTPS, an important first step in securing any data your website collects, such as customer or payment information. Unfortunately, HTTPS is the bare minimum security requirement, and is not enough to stop cybercriminals from infiltrating your database and stealing sensitive customer information. Because a WAF uses a set of policies to filter and block unwanted web traffic as well as protect against the most common types of hacks on a continuous basis, it can help secure you in ways the HTTPS is unable to. It also helps increase site speed and performance by using caching mechanisms.
While it is wise for any organization with a web application to have a WAF, some specific types of organizations who may be more prone to web attacks include:
-E-commerce sites
-Online financial services
-Lead generation sites
-Online healthcare services
-Any organization required to follow compliancy standards such as PCI DSS or HIPAA.
Read 8 things to ask every backup & disaster recovery provider.
Benefits of a Web Application Firewall
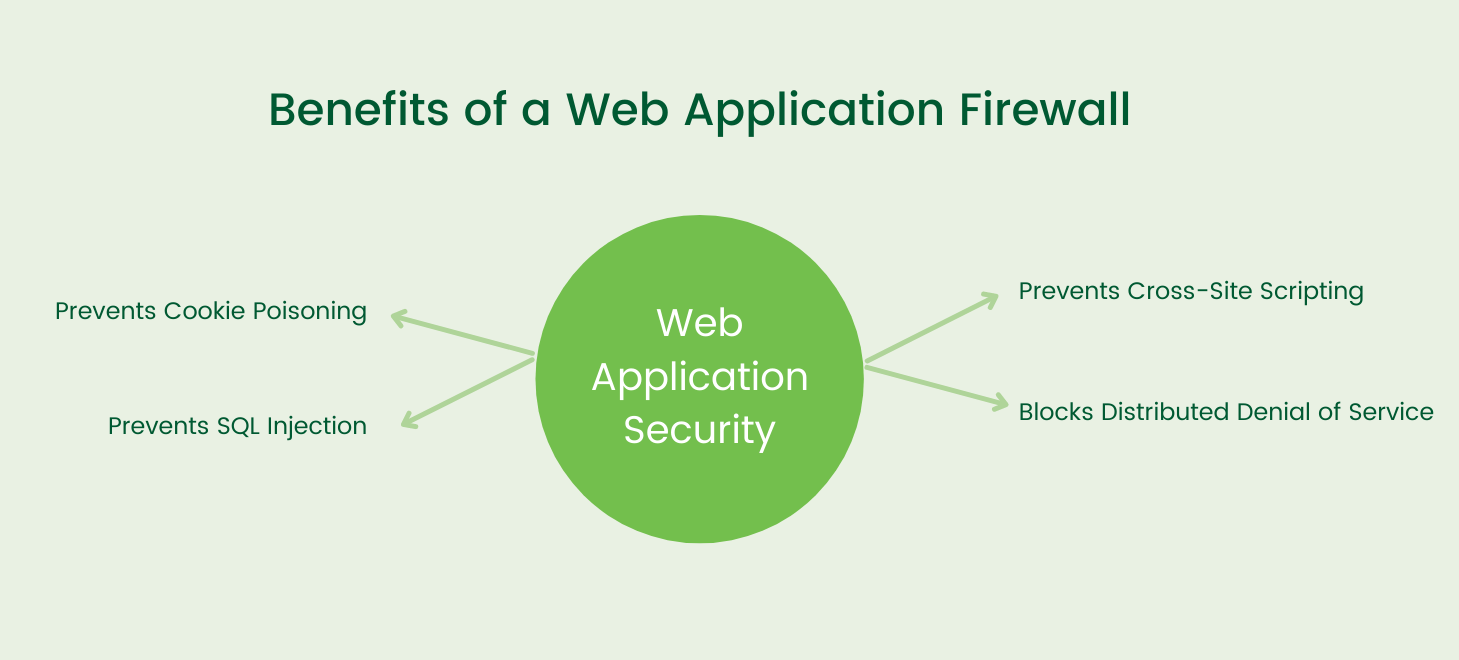
WAFs, while not a total security solution itself, play a role when creating a robust and comprehensive security structure. It will monitor and block unwanted traffic to a web application that a firewall alone will not block. It is easy to install, deploy, and maintain , particularly if you select the software-as-a-service option, and help fill in the security that your regular firewall lacks.
Without a WAF, your organization can face a cybersecurity attack that result in leaking sensitive customer or business data, losing your reputation and customer trust, and even having your website be blacklisted on search engines. Altogether, the impact of this would be devastating for any organization. WAFs can help protect your organization from these types of web application specific cyberattacks such as:
Prevents Cookie Poisoning
Cookie poisoning, also known as session hijacking, is when a cybercriminal manipulates or forges a cookie to bypass security or gain access to the server to steal data. This type of attack is used when a user is required to login to an account and the cybercriminal intercepts the cookie to extract saved information from it, such as auto-filled personal information. WAFs can prevent this from happening by protecting and encrypting personal identifiable information as well as identifying altered or "poisoned" cookies from reaching the server.
Prevents SQL Injection
SQL stands for Structured Query Language and is a common programming language. SQL injection is when a cybercriminal modify queries an application makes which can grant them access to important personal or financial information. WAF can prevent against this by running off rules that require SQL injections to match specified conditions and if they do not, it will block the user from even reaching the web application.
Prevents Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Similar to cookie poisoning, Cross-Site Scripting, or XSS, is a type of injection involving malicious scripts. Cybercriminals send malicious code through the web application directly to a different end user to attempt to access cookies or other sensitive data saved in the browser and used by the web application. WAF can help prevent against this with configured policies to scan and monitor these requests and block them when safe conditions are not matched. If identified by the WAF as malicious XSS code, it will block it from gaining access.
Blocks Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
This type of attack involves several devices that have been infected with malware overwhelming a web application by creating an unusual amount of traffic. This causes a denial-of-service to normal traffic, cause performance issues, and weaken the layers of security. A WAF can identify and block this type of unusual activity based on key indicators such as high levels of traffic from a single IP address, unusual traffic matters, or high traffic on a specific page.
Learn how to keep your business safe from wildfires and other disasters.
Conclusion
While your organization's firewall, backup and recovery plan, and other security features are crucial to maintaining a secure infrastructure, a WAF can help fill in the security gaps you might be facing. Not only will it protect and even improve your website's performance, it can help protect your customer's sensitive personal and financial data from cyberattacks such as SQL injections and DDoS. If your organization is required to follow compliancy standards such as HIPAA or PCI DSS, a WAF can help meet these standards and add to your robust security infrastructure.
Interested in learning more about Web Application Firewalls? Contact us today to get your questions answered.


-png.png?width=300&name=Web%20Application%20Firewall%20(2)-png.png)